
We have published a paper where we investigate the stability of persistent currents in superfluid fermionic gases confined to a ring. Our findings reveal two critical thresholds relevant for stability of persistent currents: one due to vortex proliferation and another from pair-breaking effects.
See article here
New open-source software provides a versatile environment for quantum numerical simulations of the dynamics of the inner crust of superfluid neutron stars. Our new article presenting this software was published in Phys. Rev. X.

In our paper, Phys. Rev. Research 6, L042003 (2024), we have shown that the unitary Fermi gas is a pure quantum many-body system with no classical limit, relevant to the physics of neutron stars, nuclei, cold atoms and condensed matter systems, in which quantum turbulence and non-Markovian dynamics coexist and there is an unexpected slow rate of eigenstate thermalization.
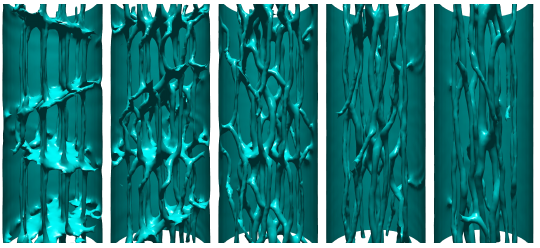
Under some conditions dynamics of quantum vortices may become chaotic and leads to a new type of behavior called quantum turbulence. Aim of these studies is to better understand the dynamics in strongly interacting Fermi systems.
See my recent talk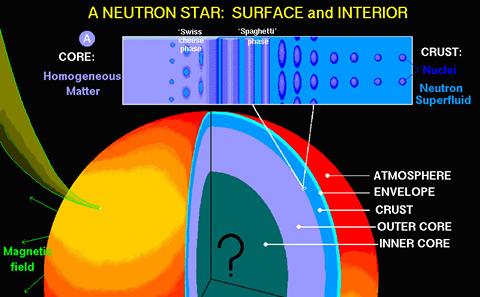
Despite 40 years of studies of neutron stars, detailed mechanism for glitches remains a puzzle. Together with researchers from CAMK we try to construct reliable model of this mysterious astrophysical phenomena.
See my recent talk
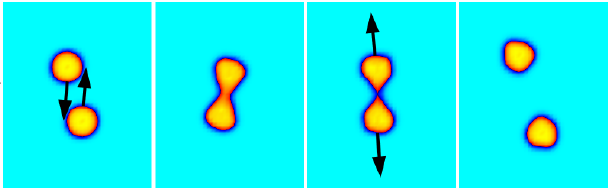
Recently, we have reported a novel role of pairing in low-energy heavy ion reactions at energies above the Coulomb barrier, which may have a detectable impact on reaction outcomes. The effect is under further investigation.
See our paper with simple explanation of the effectCheck Top500 for present ranking of supercomputers

LUMI @ CSC’s data center in Kajaani (Finland) - One of the pan-European pre-exascale supercomputers.

Piz Daint @ Swiss National Supercomputing Centre (Switzerland) - Access is granted thanks to PRACE.
See article at CSCS webpage
Summit @ Oak Ridge National Laboratory (USA) - presently the fastest world computing system. Access is granted thanks to ASCR program.
My group develops W-SLDA Toolkit: a self-consistent solver of mathematical problems which have structure formally equivalent to Bogoliubov-de Gennes equations. The toolkit is designed to solve problems related to fermnic superfluidity
My group invites computer scientists who would like to get involved in researches that combine Physics & Supercomputing. See here for more details...
dr hab. inż.
Gabriel Wlazłowski

ul. Koszykowa 75, Warsaw 00-662, Poland
office: 226B
e-mail: gabriel.wlazlowski@pw.edu.pl
tel: (+48) 22 234 5439
Last update: 04-12-2024
Faculty of Physics @ WUT